Yes, you can trade without a VAT number if your VAT-taxable turnover is £90,000 or less. Businesses that fall in this threshold can register themselves for VAT numbers, but it is not mandatory.
Is your business operational in the UK, and you don’t know whether you have a valid VAT number or not? This issue can further lead to the inability to claim the VAT back for the goods and services you buy. Thus, make sure to check UK VAT number to avoid all the restrictions.
So, without any further disclosure, let’s see the different ways to check if your business has a valid VAT number by first understanding what a VAT number is.
Understanding VAT Number

A VAT number or value-added tax is an identifier assigned to businesses with the purpose of collection, payment, and reporting of the company’s value-added tax. Businesses often require professional business accounting services to ensure compliance with VAT regulations.
Similar to the payroll number, the VAT number is also used for tax purposes. The only difference between the two is that VAT is used to collect or reclaim the value-added tax on sales of goods and services, whereas payroll is used to manage the payroll and tax deductions within company systems. For businesses managing payroll, payroll services in the UK can help streamline tax obligations.
Countries like England, Wales, and Scotland mostly have an 11-digit VAT number beginning with the letter “GB,” followed by 9 numbers. For example, GB987654321.
Enough disclosure about the VAT number. The next informative aspect that everyone should know is registering their company for a VAT number. Read the subsequent section to get an overall glimpse of the process of registering your company for a VAT number.
How to Check the UK VAT Number of Your Company?
There are particularly two different methods to check VAT number of your business. Carefully go through the methods to check the validation of any company’s VAT number correctly.
1. HM Revenue & Customs Website
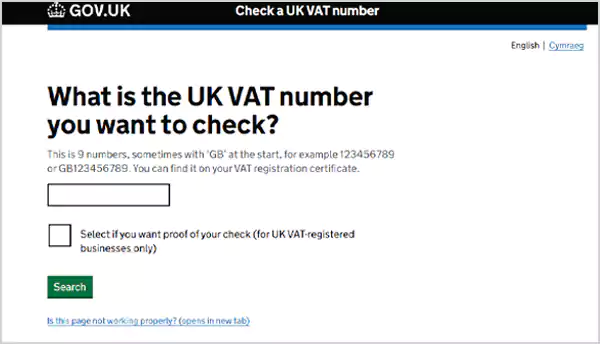
To check whether your VAT number is valid or not, you need to visit the official website of HM Revenue & Customs and navigate to the “Check a UK VAT Number.” page. Scroll down, click on the “Start now” option, and just enter your VAT number.
If the VAT is identified and information like your business name and address are shown on the screen, it means your VAT number is valid.
Moreover, this service also offers a certification of authenticity to prove that the VAT number is valid at a certain time and date. Generally, this certificate is mainly useful for newly set up businesses and when occupying new suppliers. If your business needs assistance, bookkeeping services for businesses can help maintain financial records efficiently.
2. European Commission VAT Validation
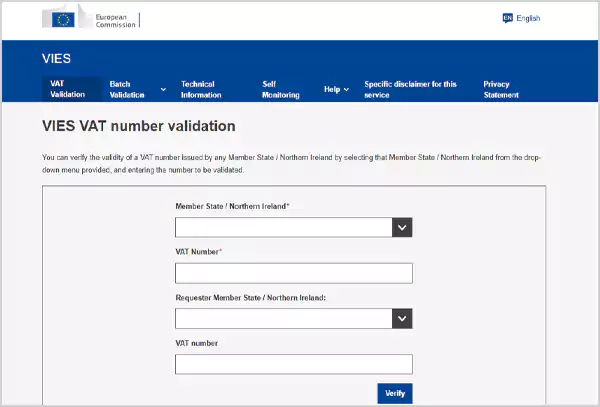
Another way to verify if your VAT is valid is by using the VIES VAT number validation on the official website of the European Commission. Visit the page and enter your member state or Northern Ireland along with your respective VAT number. Finish the process by clicking the verify button at the bottom.
It will verify if your VAT number is valid or not by displaying the details of the associated business.
How Do You Register Your Company for VAT Number?
To register your company for VAT, you need to first understand the right approach. The registration process mainly includes 4 different steps. So, carefully read the below-mentioned steps to avoid skipping any crucial information.
1. Eligibility Requirement
The first and foremost step in VAT registration of your company is determining the eligibility of your company. This comes with assessing the turnover of VAT taxability of your establishment. In the UK, if a company’s taxable VAT turnover is more than £90,000 in 12 months or the anticipated yearly turnover as per the one-month records, VAT registration is compulsory for the company.
Businesses can still register their businesses for VAT even if they don’t reach the threshold. When registering, businesses must also keep up with accounts payable services in the UK to manage vendor payments and financial transactions.
2. Online Registration
Almost all VAT registration in the UK is done via the online portal of the HMRC. But before that, you need a Government Gateway user ID. This ID will be used to submit your VAT returns to the HMRC. To create your Government Gateway user ID, you need the following:
- An email address.
- A confirmation code will be sent by the HMRC to the email address.
- Your full name.
- An 8- to 12-character password.
- A recovery password.
After following all these steps, you will be provided with your Government Gateway user ID. It allows you to save your progress and register later on.
3. Waiting for Confirmation
After the successful submission of the application to the HMRC portal, you will receive a confirmation email that will include a reference number. This reference number is also your VAT number that will be used to track the progress of your application until you receive your actual VAT number.
In most cases, all the applications receive their VAT number within the span of 2 weeks. Therefore, the validity of the reference number is also 2 weeks. If you don’t receive any updates from the HMRC regarding the VAT number, contact the HMRC’s Registration Team via email: vrs.newregistrations@hmrc.gov.uk.
However, even while waiting for confirmation, you can still set up your VAT accounting system.
4. VAT Accounting Set Up
Setting up VAT accounting is concerned with understanding the trigger point for the VAT liability. There could be different trigger points for the VAT liability; each requires a different accounting setup.
- VAT Flat Rate Scheme: For small businesses with an annual taxable turnover of £150,000 or less, excluding VAT.
- VAT Annual Accounting Scheme: If your annual VAT taxable turnover is £1.35 million or less and only fills one VAT return once a year instead of 4.
- VAT Cash Accounting Scheme: For businesses whose annual taxable turnover is £150,000 or less, excluding VAT, and pay VAT immediately to the HMRC instead of after invoicing them.
- VAT Margin Scheme: If you are a retail business or sell second-hand goods and pay VAT on the value added to the selling price of goods.
Importance of Checking VAT Registration Number
Checking the VAT number of both your business and associating business holds great significance in business transactions. Therefore, we have mentioned the importance of checking your VAT number.
- Protect VAT Claims: A VAT number guards your VAT claiming ability on eligible expenses, as claims made from invalid numbers are not claimable.
- Compliance with VAT: Checking the VAT number of the associating companies ensures that the dealing is meeting the regulatory standards.
- Safeguards against Frauds: There is a high chance that companies that use invalid VAT numbers are dealing in fraudulent transactions. So, make sure to check whether the VAT number of a dealing business is valid or not.
- No Restrictions in International Trade: Checking the VAT number also helps in the smooth facilitation of international trade without any cross-border restrictions.
- Bring Reliability: A valid VAT number heightens trust among the suppliers and customers.
VAT Number vs. UTR Number: What’s the Difference?
While shedding light on all confusion regarding the VAT number, our focus falls on the similarities of the UTR number with value-added tax (VAT), which has perplexed people into thinking that these are the same. But actually, both are completely different from each other.
The UTR number is a 10-digit number issued by the HMRC to individuals and companies for tax purposes. This number is specifically assigned for registering as self-employed. Many self-employed individuals also need to keep track of their profit and loss statements for accurate tax reporting.
On the other hand, the VAT number is an 11-digit number, assigned to businesses only. The purpose of this identifier is to mainly support the VAT taxation of the business. It’s primarily used for submitting VAT returns and filling out VAT invoices.
This confusion is raised as both the numbers are issued by the HMRC and used for tax purposes. However, businesses often need to address more than just VAT and UTR concerns, as financial complexities like corporate debt restructuring also play a vital role in managing overall financial health.
Wrapping Up
Although registering your business for a VAT number is not mandatory for all corporations, doing so opens up various growth opportunities. This mostly includes business dealings comprising transactions. But this only applies to businesses with valid VAT numbers. Hence, make sure to check UK VAT number of your business. If it’s not valid, immediately contact HMRC and share your concerns. Business confirmation statement filing services can help companies meet compliance requirements. Similarly, dormant businesses must still fulfill tax obligations, and dormant accounts filing services ensure financial records remain accurate.
For companies managing both VAT returns and self-assessment tax filings, seeking self-assessment tax return services in the UK can simplify the process. Additionally, businesses involved in sales must ensure proper invoicing and debt recovery. Accounts receivable services in the UK provide structured financial tracking for incoming payments.